You
what is consistent-hashing-in-system-design
ChatGPT
Consistent hashing is a technique used in distributed systems and system design to efficiently distribute data across a set of nodes while minimizing the amount of data that needs to be reorganized when nodes are added or removed. This helps in achieving load balancing and fault tolerance in distributed systems.
In a traditional hashing mechanism, adding or removing a node can significantly affect the distribution of data, leading to a need for rehashing and redistribution of data across the nodes. Consistent hashing aims to address this issue by providing a way to map keys to nodes in a way that minimizes the amount of remapping required when the number of nodes changes.
Here's a basic overview of how consistent hashing works:
Mapping Keys to Nodes:
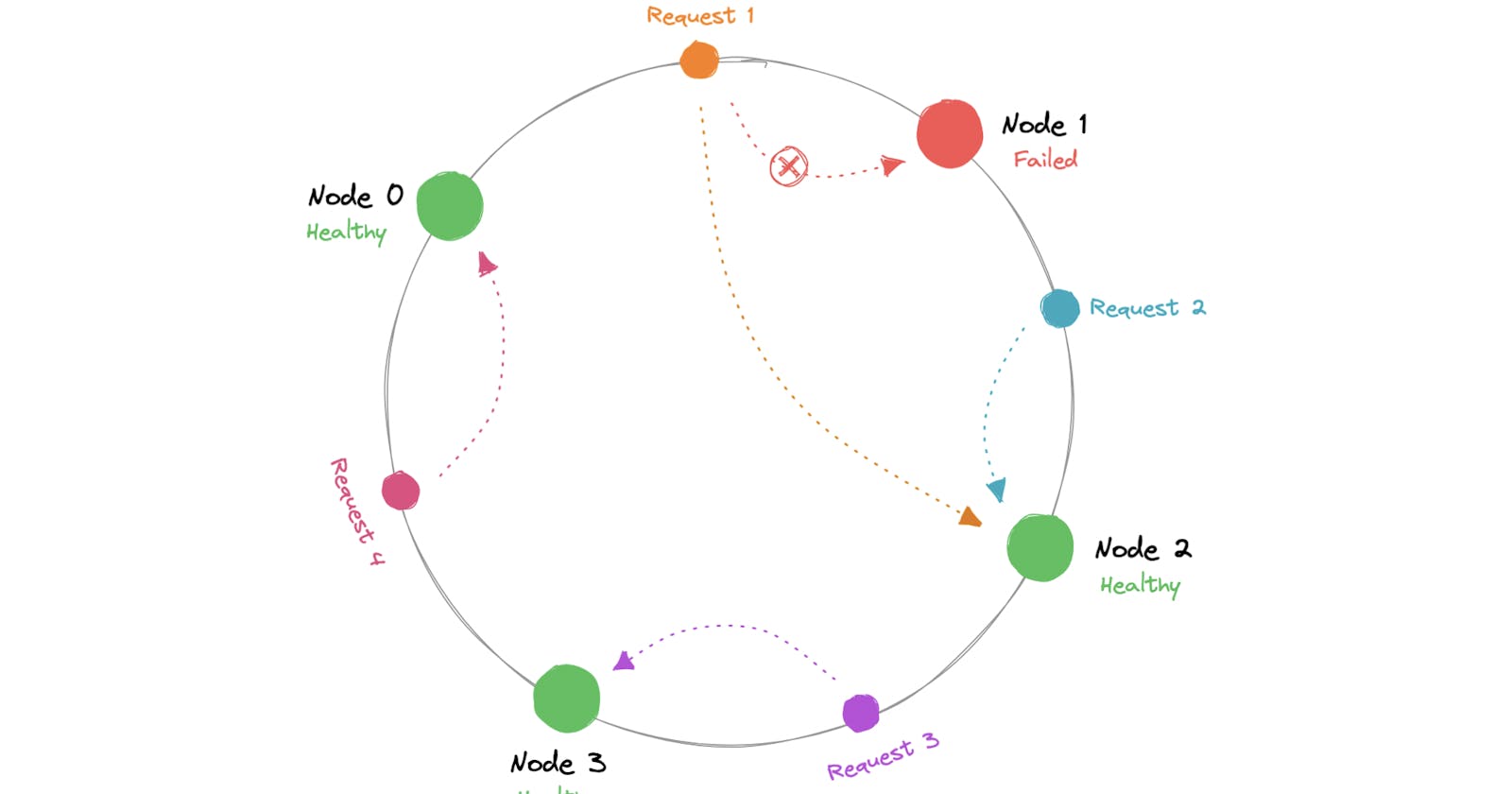
The hash space is considered as a ring, where each node and key is assigned a position on the ring based on their hash values.
Each key is hashed to a position on the ring.
Assigning Nodes:
Nodes are also assigned positions on the ring based on their hash values.
The ring is divided into segments, with each node responsible for the keys in its segment, moving clockwise.
Finding Node for a Key:
To find the node responsible for a key, you hash the key and find its position on the ring.
Moving clockwise from that position, you find the first node encountered, and that node is responsible for the key.
Adding or Removing Nodes:
When a node is added or removed, only a small portion of the keys needs to be remapped.
Keys that were originally assigned to the node being added or removed are the ones affected.
Load Balancing:
- Consistent hashing helps distribute keys evenly across nodes, providing a form of load balancing.
Fault Tolerance:
- In case of node failures, consistent hashing minimizes the impact on the system as only the keys assigned to the failed node need to be remapped.
Consistent hashing is widely used in distributed storage systems, such as distributed databases, content delivery networks (CDNs), and distributed caches, where the ability to scale the system dynamically and handle node failures without major disruptions is crucial. It reduces the amount of data movement needed during node changes, making the system more robust and scalable.
You
didn't understand what keys is, what is being hashed, give a very simple example to explain this concept
ChatGPT
Certainly! Let's simplify the concept of consistent hashing with a straightforward example.
Imagine you have a distributed storage system with three nodes (A, B, and C) forming a ring. We'll use numbers as keys, and each key needs to be stored in the system. The goal is to distribute these keys across the nodes in a balanced way.
Assigning Nodes:
- Nodes A, B, and C are placed on a circle (hash ring) based on their hash values.
codeA ---------- B ---------- C
Mapping Keys:
- Keys (numbers) are also hashed and placed on the ring. For simplicity, let's say key 5 hashes to a position between nodes A and B.
codeA ---------- (5) -------- B ---------- C
Finding the Responsible Node:
- To find the node responsible for a key, you move clockwise from the key's position until you reach the first node. In this case, it's node B.
Adding a Node:
- Now, let's say you want to add a new node, D, to the system. When you add D, it gets placed on the ring based on its hash value.
codeA ---------- (5) -------- B ---------- C
|
D
- Since node D is inserted between A and B, only keys in the segment between A and D need to be remapped. The rest of the keys remain unchanged.
Removing a Node:
- Similarly, if you want to remove node B, only keys in the segment between A and C need to be remapped.
codeA ---------- (5) --------------------- C
|
D
In this way, consistent hashing minimizes the amount of data that needs to be moved around when nodes are added or removed. The keys are hashed onto the ring, and the nodes are responsible for the keys in their respective segments. This allows for a scalable and fault-tolerant distribution of data in a distributed system.